An Introduction to Micro Gear Pumps
Micro gear pumps are essential components in many systems requiring precise fluid control. These devices operate under a principle that involves meshed gears rotating to create a vacuum that draws in fluid and subsequently displaces it from the outlet. Being compact, they are widely utilized in various applications where space is a constraint and accuracy is paramount. As beginners venture into the world of micro gear pumps, it’s important to understand not only what they are but also the history, mechanics, and various types prevalent in the industry today.
Basics of a Micro Gear Pump
A micro gear pump essentially consists of two or more synchronized gears that mesh together, enabling the movement of fluid. The design typically facilitates minimal space usage while maximizing performance. Due to the intricacy in their design, these pumps provide a continuous and smooth flow of liquid, which is crucial in applications demanding uniformity. Additionally, they are positive displacement pumps, which means they move a consistent volume of fluid through the system regardless of the pressure.
Historical Development of Micro Gear Pumps
The inception of gear pumps dates back to the early 20th century when engineers began experimenting with various mechanisms to enhance fluid transfer efficiency. The emergence of micro gear pumps occurred with the growing need for compact designs in industries such as automotive, pharmaceutical, and electronics. Over the decades, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have significantly increased their reliability and application range while introducing automation into their operation systems.
How Micro Gear Pumps Work
Fundamental Working Principles
Micro gear pumps operate on a fundamental principle of mechanical energy conversion into fluid motion. When the gears rotate, they create a vacuum on the inlet side, drawing fluid into the pump chamber. As the gears continue to turn, they progressively push the fluid through the outlet. The unique design of these pumps minimizes turbulence and encourages laminar flow, ensuring a consistent delivery rate. It is the precision in the gear alignment that fosters the high efficiency characteristic of micro gear pumps.
Key Components and Their Functions
Key components of micro gear pumps include the gears themselves, a housing unit, bearings, and seals. The gears are responsible for moving the fluid, whereas the housing provides structural integrity and encasement for the fluid being transferred. Bearings facilitate smooth rotation of the gears at high speeds, and seals are critical in preventing leaks and ensuring the integrity of the fluid path. Each component must be meticulously designed and manufactured to withstand the operational stresses these devices encounter.
Types of Micro Gear Pumps
Classification Based on Design
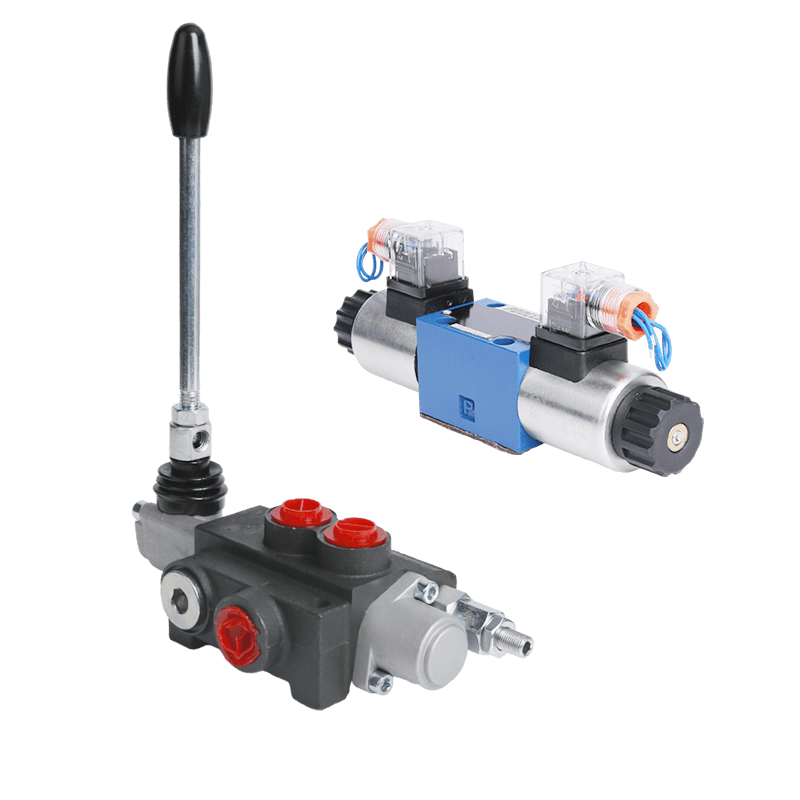
Micro gear pumps can be primarily classified into two categories based on their design: external gear pumps and internal gear pumps. Understanding the difference between these types is crucial for selecting the right pump for a specific application.
External Gear Pumps
External gear pumps consist of two gears mounted on parallel shafts. The gears rotate against each other, drawing liquid into the pump chamber from the inlet port and displacing it through the outlet. These pumps are commonly used in applications where higher flow rates are needed, and their simplicity facilitates easy maintenance. They are often utilized in hydraulic systems and lubrication processes.
Internal Gear Pumps
Internal gear pumps have one gear inside another, which creates a unique configuration enabling fluid transport. These pumps are known for their ability to handle more viscous fluids and provide a consistent flow rate even under varying pressure conditions. They are particularly suited for applications involving chemicals and fuels where precision and control are essential, showcasing their versatility across different industries.
Applications in Various Industries
Micro gear pumps find their place in a variety of industries due to their precision and adaptability. In the pharmaceutical industry, they are used for dosing precise amounts of liquids during the manufacturing process. In the automotive sector, these pumps are often involved in transferring fuel or lubricants. Additionally, inkjet printing relies on micro gear pumps for the precise delivery of ink, showcasing their operational importance across diverse fields.
Advantages and Limitations of Micro Gear Pumps
Benefits in Industrial Use
The advantages of micro gear pumps are substantial. They provide accurate fluid control, which is especially important in processes requiring high precision. Their compact design allows for easy integration into systems with limited space, and their reliability ensures minimal downtime during operations. Furthermore, these pumps are capable of handling a variety of fluids, making them versatile tools in many industrial applications.
Common Challenges and Issues
Despite their numerous benefits, micro gear pumps are not without challenges. They can be sensitive to particle contamination, which may lead to wear and degradation of the components. Additionally, heat generation during operation can affect performance and longevity if not managed properly. Understanding these limitations is important for effective maintenance and operation within various industrial environments.
Selecting the Right Micro Gear Pump for Your Needs
Factors to Consider
Flow Rate Requirements
When selecting a micro gear pump, it is crucial to consider the required flow rate for your specific application. Flow rate is measured in liters per minute or gallons per minute and dictates how much fluid the pump must move within a set timeframe. Each micro gear pump model can handle different flow rates, and exceeding this limit can lead to pump failure or inefficiency. Understanding the flow requirements allows you to choose a pump that will operate within optimal conditions, ensuring longevity and ideal performance.
Material Compatibility
Material compatibility is another vital consideration. Micro gear pumps come into contact with various fluids, and the materials used in the pump’s construction must withstand the chemical properties of those fluids. For instance, if the pump is used to transfer corrosive liquids, components made of highly resistant materials such as stainless steel or specific polymers should be selected. Ignoring material compatibility can lead to pump degradation, leaks, or malfunctions, ultimately affecting the entire system.
Pressure Ratings
Pressure ratings provide essential information about the operational limits of a micro gear pump. Each pump is designed to operate within specified pressure ranges, and exceeding these ratings can cause significant mechanical stress, leading to performance issues or failure. Understanding the pressure demands of your application is critical when choosing a micro gear pump. It is advisable to select a pump that not only meets these pressures but also offers a safety margin to accommodate unexpected fluctuations in system requirements.
Size Constraints
Finally, size constraints can significantly influence which micro gear pump to implement in a given setting. Various industries often face spatial limitations, and it is vital to select a pump that fits within the available dimensions without compromising on performance. Assessing both the physical size of the pump and the space in which it will be installed ensures that the pump can operate efficiently without causing obstructions or requiring modifications to existing infrastructure.
Maintenance and Care for Micro Gear Pumps
Routine Inspection Tips
Routine inspections are fundamental for maintaining the functionality of micro gear pumps. Regular checks can help detect potential issues before they escalate into serious problems. Inspecting for leaks, unusual noises, or changes in performance is essential for early detection of wear or damage. This proactive approach can help extend the life of the pump and maintain overall system integrity, ensuring dependable and continuous operation.
Preventive Maintenance Practices
Preventive maintenance practices for micro gear pumps encompass various activities centered around sustaining optimal pump performance. Regularly changing lubricants, ensuring proper alignment of components, and confirming that seals remain intact are integral to this process. Furthermore, using filters to prevent particulate contamination can significantly reduce wear on critical components. Implementing a structured maintenance schedule can foster better operational efficiency and reduce unplanned downtime.
Poocca: A Leading Brand in Micro Gear Pump Technology
Overview of Poocca’s Product Range
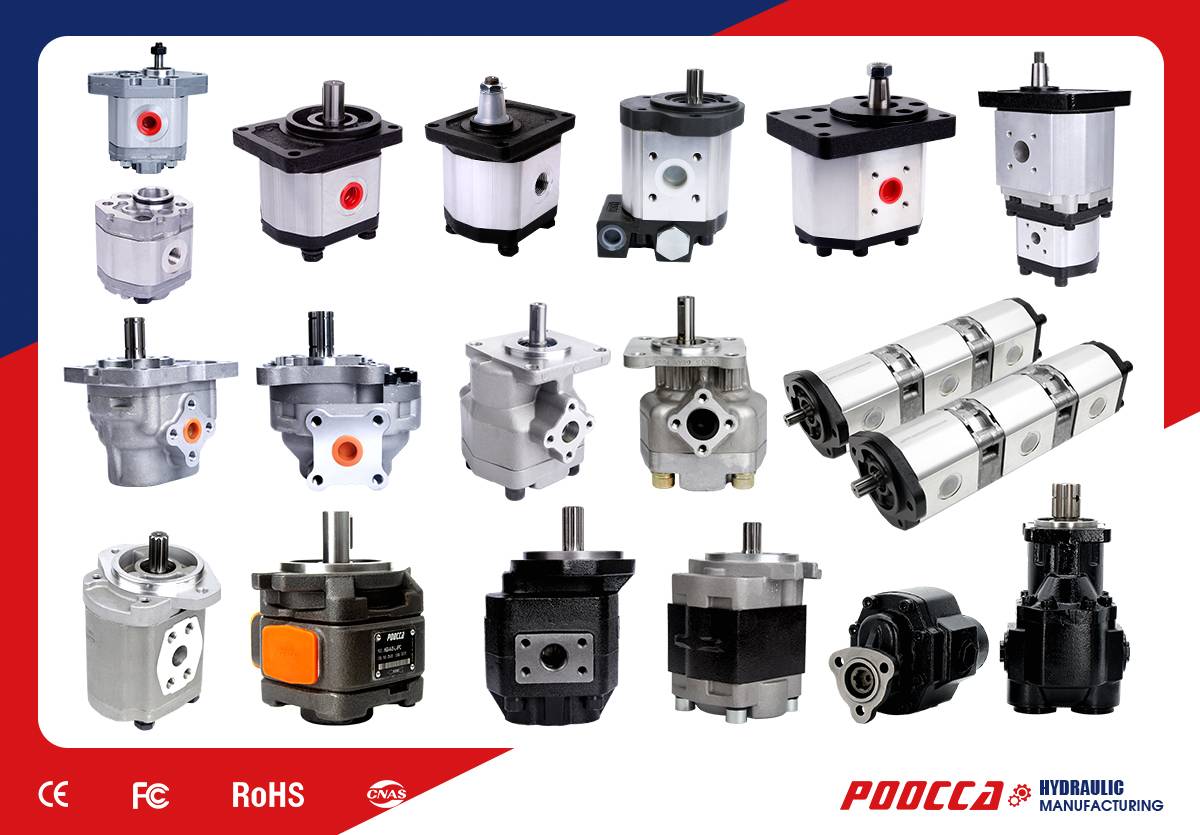
Poocca stands out as a reputable brand in the micro gear pump market, known for its innovative approach and extensive product range. The company offers a variety of micro gear pumps tailored for different industrial applications, demonstrating versatility and adaptability in design. With an emphasis on quality and precision, Poocca’s products cater to a wide array of needs, from chemical delivery systems to laboratory equipment. This broad selection ensures that customers can find models suited to their specific requirements without compromising on efficiency.
Special Features of Poocca’s Micro Gear Pump Series
Poocca’s micro gear pump series is distinguished by several unique features that enhance usability and performance. These pumps are often equipped with advanced control mechanisms that allow for precise flow rate adjustments, making them suitable for sensitive applications. Additionally, many of Poocca’s models incorporate robust construction materials that enhance chemical compatibility and reduce wear and tear over time. With a focus on user-friendly designs, these pumps often come with easy-to-follow installation guidelines and maintenance instructions that ensure smooth integration into larger systems.
Industry-Specific Solutions Offered by Poocca
Poocca recognizes that different industries have unique requirements and challenges, which is evident in their targeted solutions. For example, their pumps designed for the pharmaceutical sector possess features that ensure the accuracy of dosing processes. Similarly, Poocca offers pumps specifically engineered for the automotive industry, emphasizing durability and reliability under high-stress conditions. By continuously engaging with industry needs, Poocca remains committed to providing tailored solutions that meet the evolving demands of their diverse clientele.
Future Trends in Micro Gear Pump Technology
Innovations and Technological Advancements
The future of micro gear pump technology is marked by rapid innovations aimed at enhancing efficiency and functionality. Advances in manufacturing techniques and materials science are paving the way for lighter, more compact designs that maintain high performance. Additionally, the incorporation of smart technology in pump systems allows for real-time monitoring and control, optimizing process parameters and reducing waste. By leveraging these technological advancements, micro gear pumps are expected to become even more integral across various applications, supporting the movement toward automation and precision engineering.
Emerging Applications and Markets
Emerging applications for micro gear pumps reveal new markets that challenge traditional limitations. The increasing demand for micro fluidics in sectors such as medical devices and diagnostics illustrates the pump’s adaptability to smaller scale operations. Moreover, the growth of environmentally friendly technologies and renewable energy systems is likely to create new niches for micro gear pumps, particularly in bioprocessing and renewable fuels. As industries evolve and explore innovative solutions to meet global challenges, the scope of micro gear pump technology continues to broaden, ensuring relevance in a dynamic market landscape.