Understanding Hydraulic Cylinder Seals
Functions and Importance
Hydraulic cylinder seals play a role in upholding the effectiveness and durability of systems by preventing fluid leakage and maintaining the required pressure for operation within the system. Moreover, they also act as a barrier against contaminants to safeguard components from wear and tear. Maintaining sealing is essential for ensuring the efficiency and dependability of cylinders since even small leaks can result in substantial inefficiencies, during operation and higher maintenance expenses.
Main Types of Hydraulic Seals
Hydraulic seals can be categorized into several types based on their function and position within the cylinder. The primary types include:
- Rod Seals: These are positioned at the cylinder head and prevent fluid leakage from within the cylinder.
- Piston Seals: Located between the piston and cylinder bore, they maintain pressure by preventing fluid bypass.
- Wiper Seals: Positioned externally, they prevent dirt and debris from entering the cylinder during rod retraction.
- Static Seals: Used in non-moving parts to maintain a seal between two surfaces.
- Guide Rings: Although not seals per se, they support side loads and prevent metal-to-metal contact.
Every kind of component has its function, in maintaining the hydraulic system’s smooth operation and preventing leaks or contamination.
Materials Used in Hydraulic Seals
Overview of Material Types
The selection of materials, for seals, plays a role, in determining how well they perform and how long they last when used with various fluids; typical options include;
- Elastomers (e.g., Nitrile Rubber, Fluorocarbon): Known for flexibility and resistance to wear; suitable for various temperatures.
- Polyurethane: Offers excellent abrasion resistance; ideal for high-pressure applications.
- PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): Provides low friction and chemical resistance; used in dynamic applications.
- Metallic Materials: Occasionally used in applications requiring extreme strength or heat resistance.
Choosing the right material hinges, on aspects, like the temperature of operation the pressure involved, the type of fluid being used, and the prevailing environmental conditions.
Principles of Hydraulic Cylinder Operation
Definition and Basic Principles
In equipment and machinery setups is a hydraulic cylinder—a mechanical device driven by pressurized hydraulic fluid to generate linear motion and force by converting fluid energy into mechanical energy.
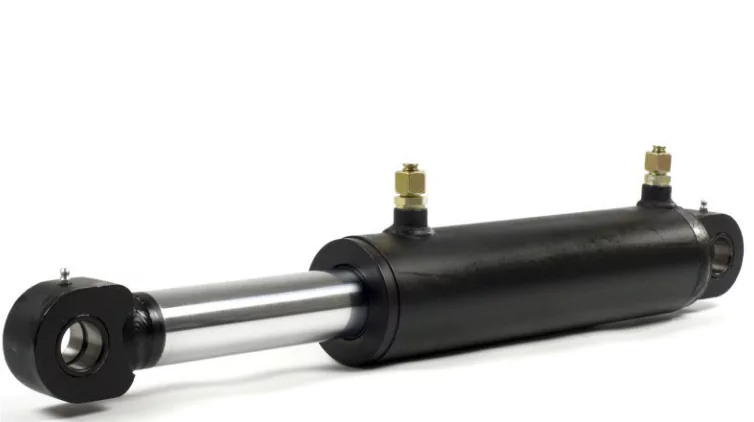
Main Parts of a Hydraulic Cylinder
The key elements of a cylinder comprise;
- Cylinder Barrel: Houses the piston and holds the pressurized fluid.
- Piston: Moves back and forth within the barrel to transfer force.
- Piston Rod: Connects the piston to external machinery or load.
- Cylinder Head/Cover: Seals one end of the barrel; contains rod seals.
- Cylinder Base/Cap: Closes off the other end of the barrel; may contain ports for fluid entry/exit.
These components collaborate to enable motion in systems.
How Hydraulic Cylinders Work
Role of Hydraulic Fluid and Pumps
Hydraulic cylinders work by using compressible liquid from pumps to create motion in a system of chambers and pistons, within the mechanism itself.
Operation Steps
- Fluid Pressurization: The hydraulic pump draws fluid from a reservoir, pressurizing it before directing it into the cylinder through control valves.
- Piston Movement: Pressurized fluid enters one side of the piston chamber while exiting from another side through return lines; this differential pressure causes piston movement.
- Load Transfer: The piston rod extends or retracts as needed to move an external load or perform work.
- Return Stroke: Reversing valve positions change fluid flow direction, allowing return stroke by pressurizing the opposite chamber.
By grasping these principles engineers have the ability to create systems that optimize efficiency and reduce strain on parts such, as seals. Regular upkeep guarantees sustained effectiveness, over time avoiding any interruptions caused by seal malfunctions or hydraulic cylinder leaks.
Enhancing Performance with Advanced Technologies
Piston Rod Construction and Coatings
The design of the piston rod is crucial, for ensuring cylinders work effectively and last long term in operation settings; manufacturers often opt for materials like hardened steel or chrome-plated steel to enhance durability and combat wear and tear issues effectively. Chrome plating is a choice due to its ability to resist corrosion and minimize friction levels within the system. Factors that contribute significantly to operational efficiency. Moreover, advanced coatings such, as diamond-like carbon (referred to as DLC) when applied can elevate the cylinder’s lifespan further by offering superior hardness and protecting against abrasive particles that may cause wear over time.
Innovations in Seal Design
Improving Seal Efficiency
In the developments of seal technology advancements aim to improve their effectiveness by reducing leaks and extending their durability lifespan. For instance, Multiple lip seals provide sealing points to minimize leakage even in high-pressure environments. Also the incorporation of materials, like elastomers enables seals to preserve their characteristics across a wider spectrum of temperatures and pressures. These upgrades do not only bolster system dependability but also cut down on maintenance expenses by stretching out the time, between seal changes.
POOCCA Integration in Systems
Benefits of Using POOCCA Solutions
Incorporating POOCCA solutions into systems brings about benefits that greatly boost performance levels. POOCCA technology emphasizes enhancing control algorithms and system setups to achieve motion control and energy efficiency. By using sensors and feedback mechanisms POOCCA solutions facilitate real-time monitoring and adjustments maintaining performance, in different load conditions. This leads to energy usage, better precision, in positioning, and prolonged component lifespan by reducing strain on parts.
Real-world Applications of Hydraulic Systems
Industries Utilizing Hydraulic Cylinders
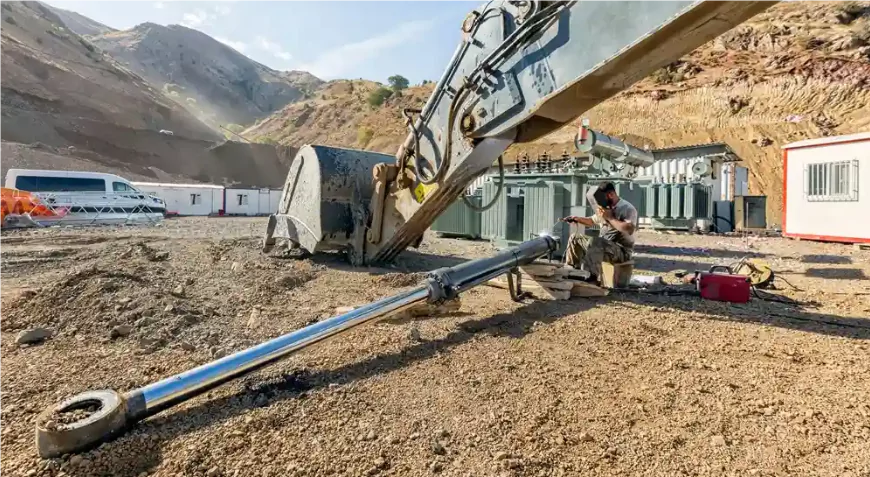
Construction Equipment
In the construction sector and heavy machinery operations, like excavators and cranes heavily depend on cylinders, for their high force outputs required for lifting and moving tasks in challenging environments with sealing technology ensuring durability and efficiency.
Automotive Industry
In the industry realm of operations and functions, like braking systems and convertible roof maneuvers majorly rely on cylinders for their pivotal functions. The accuracy provided by mechanisms is crucial for ensuring seamless performance and meeting safety regulations. Advancements in seal configurations play a role in diminishing the probability of leaks which in turn bolsters the dependability of hydraulic systems in automobiles.
Future Trends in Hydraulic Technology
Smart Hydraulics
The direction of technology is moving towards hydraulics – systems that integrate digitalization and connectivity to enhance performance monitoring and control capabilities. Intelligent hydraulics utilize sensors and IoT connections to offer, up to the minute information, on system well-being to enable maintenance approaches that minimize downtime. Furthermore implementing intelligence can adjust system settings dynamically based on operating conditions resulting in increased efficiency and lower energy consumption. With the advancement of these technologies, they have the potential to transform the way industries employ systems by providing levels of oversight and dependability.
In summary, the progress, in cylinder seal technology is still making strides in sectors by boosting efficiency cutting down maintenance expenses, and prolonging the lifespan of systems. With the use of materials, complex designs, and the incorporation of technologies such as POOCCA solutions and smart hydraulics these systems are ready to cater to contemporary needs more effectively than, in the past.