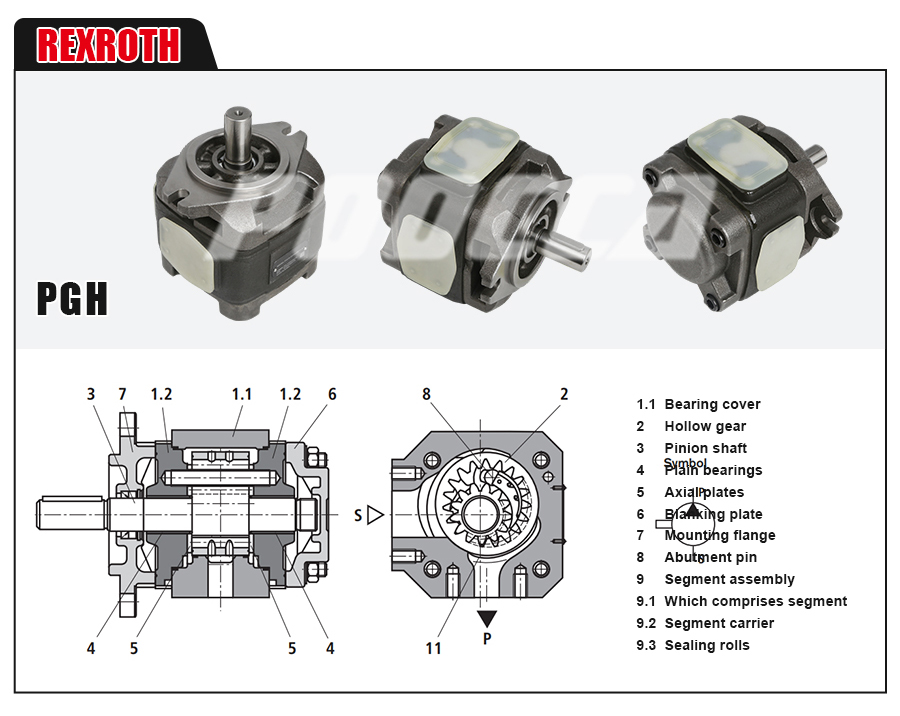
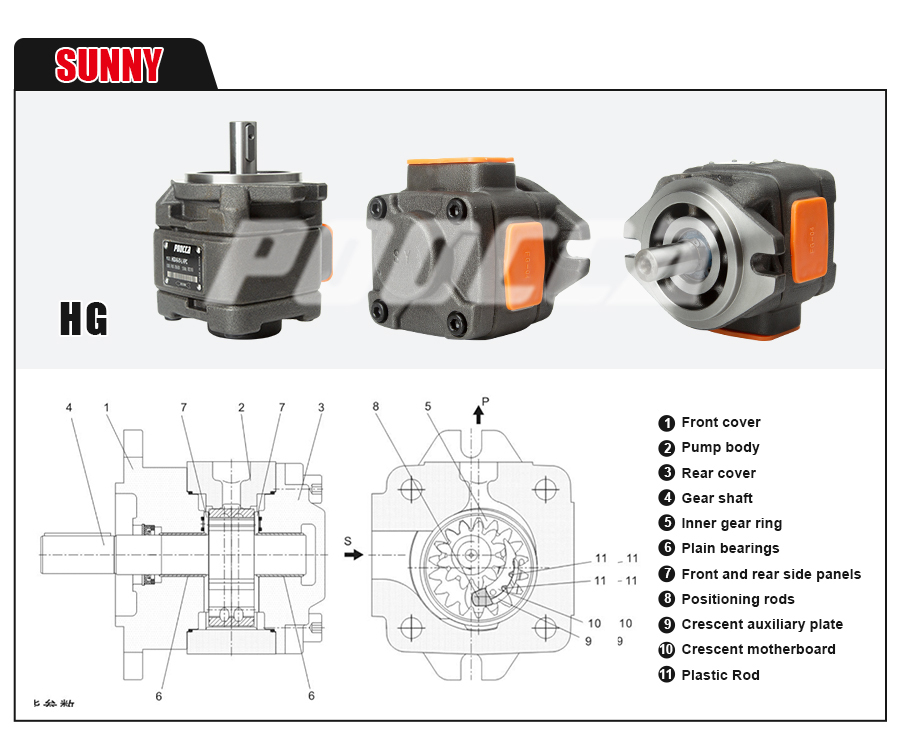
Understanding Internal Gear Pumps: An Overview
Integral to a vast array of industries, internal gear pumps are anticipated to witness considerable market expansion in the upcoming years. A study conducted by Future Market Insights (FMI) disclosed that the internal gear pump market held a value of US$ 529.1 million in 2023 and is projected to surge at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.2% throughout the prediction period. It is extrapolated that by 2034, this market could escalate to an approximate worth of US$ 857.2 million – indicative evidence of substantial demand increase and adoption escalation.
What Are Gear Pumps?
At their core, gear pumps utilize the interlocking of gears to move fluid from one place to another within a hydraulic system. The primary function of these gears is to create suction at the inlet port and draw fluid into the system before displacing it through the outlet port. This mechanism allows for efficient and reliable fluid transfer, making gear pumps a vital component in various industrial applications.
Why Internal Gear Pumps Matter
The significance of internal gear pumps lies in their versatility and widespread use across different industries. These pumps play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations in applications such as hydraulic power steering systems, lubrication systems, and fuel delivery systems. Their ability to handle high viscosity fluids with ease makes them indispensable in numerous everyday processes.
The demand for internal gear pumps continues to rise due to their efficiency, reliability, and adaptability across diverse industrial sectors. As such, understanding the intricacies of internal gear pumps becomes essential for businesses looking to optimize their fluid handling processes.
1. The Basics of Gear Pumps
Internal gear pumps are a fundamental component in various industrial applications, offering a reliable and efficient method for fluid transfer. Understanding how these pumps work and their advantages and disadvantages is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their fluid handling processes.
How Internal Gear Pumps Work
The operation of internal gear pumps relies on the interaction of two rotating gears within a tight-fitting housing. As the gears rotate, they create chambers between the teeth, which effectively trap and move the fluid from the inlet to the outlet of the pump. This mechanism results in a continuous and smooth flow of fluid, making internal gear pumps well-suited for applications requiring precise and consistent fluid delivery. The design of internal gear pumps also provides better suction capabilities, particularly for high viscosity and shear-sensitive fluids, making them an ideal choice for handling challenging liquids.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Why Choose an Internal Gear Pump
One of the primary advantages of gear pumps is their ability to handle high viscosity fluids with ease, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial processes. Additionally, internal gear pumps offer better suction capabilities compared to other types of pumps, allowing them to efficiently transfer fluids with varying viscosities. However, it’s important to note that as fluid viscosity decreases, internal gear pumps may become less efficient due to reduced lubrication between the gears.
Despite their numerous advantages, internal gear pumps also come with certain limitations. These include potential challenges in handling abrasive or corrosive fluids, as well as the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. It is essential for businesses to carefully evaluate these factors when considering the use of internal gear pumps in their operations.
2. Key Features of Internal Gear Pumps
Internal gear pumps possess unique features that make them well-suited for a wide range of industrial applications. Understanding the key aspects of pressure and flow, as well as the importance of pump size, is essential for businesses seeking to optimize their fluid handling processes.
Understanding Pressure and Flow
Internal gear pumps are known for their exceptional performance in handling high viscosity fluids. Unlike external gear pumps, which can sustain higher pressures of up to 7500 psi, internal gear pumps excel in creating better suction capabilities and are more suitable for fluids with high viscosity and shear sensitivity. This unique characteristic allows internal gear pumps to operate within a useful range from 1cP to over 1,000,000cP, making them an ideal choice for applications requiring efficient fluid transfer under challenging conditions.
The ability of internal gear pumps to maintain consistent flow rates is another key feature that sets them apart. The design of these pumps minimizes flow pulsations and noise, providing a smooth and continuous flow of fluid. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where precise fluid delivery is crucial, ensuring reliable performance across various industrial processes.
3. Selecting the Right Internal Gear Pump
When it comes to selecting the right internal gear pump, several crucial criteria must be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency in fluid handling processes. Understanding the key factors that influence pump selection, as well as common pitfalls to avoid, is essential for businesses across various industries.
Criteria for Pump Selection
Type, Size, and Shaft Seal Considerations
The first step in selecting an internal gear pump is identifying the specific type that best suits the intended application. Different types of internal gear pumps are designed to accommodate varying fluid viscosities. For instance, high-speed pumps are ideal for low viscosity fluids, while standard pumps offer versatility across a broader range of viscosities.
In addition to type considerations, selecting the right pump size is critical for achieving optimal performance. The size of an internal gear pump directly impacts its flow rate and pressure capabilities. It’s essential to match the pump size with the anticipated flow requirements of the application while accounting for potential variations in fluid viscosity and operating conditions. Proper sizing ensures efficient fluid transfer and prolongs the lifespan of the pump.
In addition, the assessment of potential shaft seal alternatives is essential when it comes to averting leakage and maintaining system integrity. The selection of an appropriate shaft seal hinges on several key factors which may include compatibility with fluids, specifically defined pressure requirements, as well as prevailing environmental conditions.
Overcoming Common Selection Mistakes
Avoiding Pitfalls in the Selection Process
One common mistake in selecting an internal gear pump is overlooking the importance of understanding specific application requirements. Failing to consider factors such as fluid viscosity, temperature variations, and system pressure can lead to suboptimal pump performance and potential operational issues. To overcome this pitfall, businesses should conduct a comprehensive assessment of their fluid handling needs and seek guidance from experienced professionals or engineers.
Another critical aspect often overlooked is neglecting long-term maintenance considerations during pump selection. While initial performance specifications are essential, it’s equally important to evaluate maintenance requirements such as seal replacements, gear inspections, and overall system upkeep. By factoring in long-term maintenance needs at the selection stage, businesses can make informed decisions that contribute to sustainable operations and cost-effective maintenance practices.
POOCCA Hydraulics is a powerful hydraulic enterprise integrating R&D, manufacturing, sales and maintenance. Its products are exported to more than 120 countries. Its quality, price and service are deeply recognized and trusted by customers.
4. Maintaining Your Internal Gear Pump
Once an internal gear pump is installed and operational, routine maintenance becomes essential to ensure its longevity, efficiency, and reliable performance. By adhering to a comprehensive maintenance schedule and following recommended procedures, businesses can prevent premature wear, damage, and breakdowns. Additionally, troubleshooting common issues promptly and implementing necessary repairs will minimize downtime and optimize pump performance.
Routine Maintenance Tips
Maintaining an internal gear pump involves several key practices that contribute to its overall health and functionality. One common misstep observed among maintenance crews is the practice of bump starting the pump to check rotation. Despite its routine nature, this approach can be detrimental. Internal gear pumps cannot operate dry, and initiating rotation without product in the pump can lead to rotor-casing friction, causing damage. This was evident in a recent customer visit, where a pump, when bump-started, resulted in scarring on the casing. Dry starts can also compromise mechanical seals. To avoid such issues, refrain from bump starting internal gear pumps without ensuring proper lubrication.
In addition to this precautionary measure, regular inspection of the pump’s components is crucial for identifying potential issues early on. This includes monitoring gear wear, checking for leaks or abnormal noise during operation, and ensuring proper lubrication levels. Implementing a proactive approach to maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the internal gear pump but also minimizes the risk of unexpected failures that could disrupt operations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When it comes to troubleshooting common issues with an internal gear pump, prompt identification and resolution are paramount. Some prevalent problems include fluid leakage at seals or connections, reduced flow rates, abnormal noise during operation, and increased power consumption. Addressing these issues promptly requires a systematic approach that involves inspecting all relevant components thoroughly.
One effective troubleshooting method involves conducting a detailed analysis of the system’s operating conditions and performance parameters. By monitoring pressure levels, flow rates, temperature variations, and overall system behavior during operation, maintenance crews can pinpoint potential irregularities and take corrective action as needed.
Furthermore, collaborating with experienced professionals or engineers for complex troubleshooting scenarios can provide valuable insights into resolving intricate issues effectively. Their expertise can help businesses navigate challenging maintenance tasks while ensuring optimal performance from their internal gear pumps.
By prioritizing routine maintenance practices and proactive troubleshooting efforts, businesses can uphold the reliability and efficiency of their internal gear pumps while minimizing operational disruptions.