Introduction to Internal Gear Pumps
Overview of Internal Gear Pumps
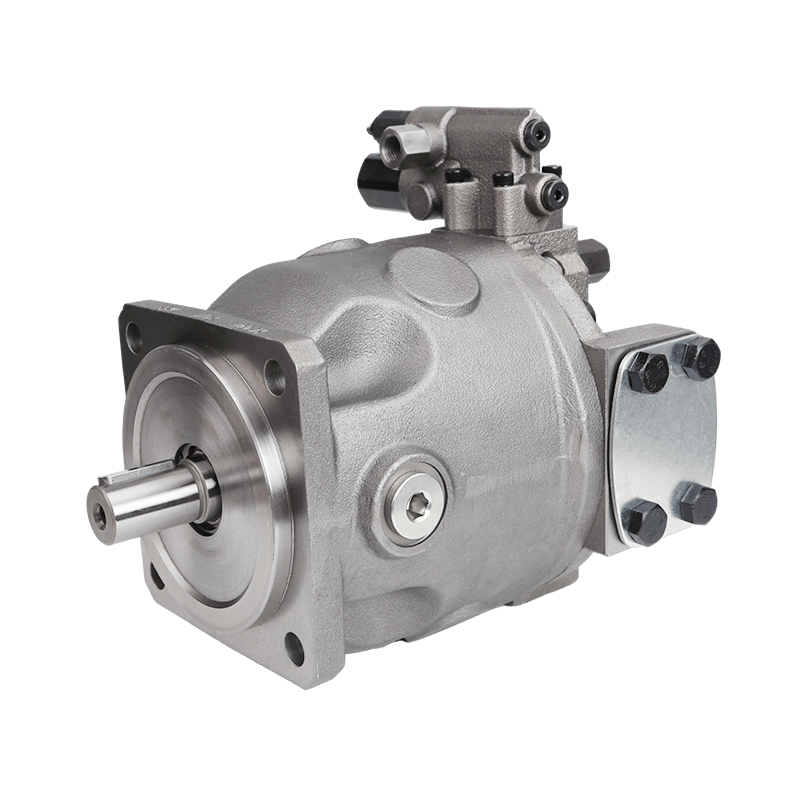
An Internal Gear Pump is a type of positive displacement pump often employed for transferring fluids with high viscosity. Its fundamental operation involves capturing fluid pockets between the gears and the pump casing, then gently moving these pockets from the suction side to the discharge side. Internal Gear Pumps are recognized for their smooth, non-pulsating flow, versatile functionality across different industries, and capability to handle a broad range of fluid viscosities.
Historical Development and Importance
The development of the Internal Gear Pump dates back to the early 20th century, driven by the need for more efficient fluid handling systems. Over decades, advancements in materials and engineering have significantly improved their efficiency and durability. In industries such as automotive, chemical processing, and food and beverage, these pumps have become integral due to their capability to handle challenging fluid dynamics with high reliability and performance.
Comparison with Other Pump Types
When comparing Internal Gear Pumps with other pump types like centrifugal pumps and external gear pumps, several advantages stand out. Unlike centrifugal pumps which are prone to cavitation at low flow rates, Internal Gear Pumps are highly efficient at maintaining a consistent flow regardless of pressure variations. Compared to external gear pumps, internal gear pumps provide a smoother flow with less pulsation and are better suited for handling higher viscosity fluids. This combination of attributes makes internal gear pumps exceptionally versatile and reliable for a broad range of applications.
The Mechanics of Fluid Flow in an Internal Gear Pump
Anatomy of an Internal Gear Pump
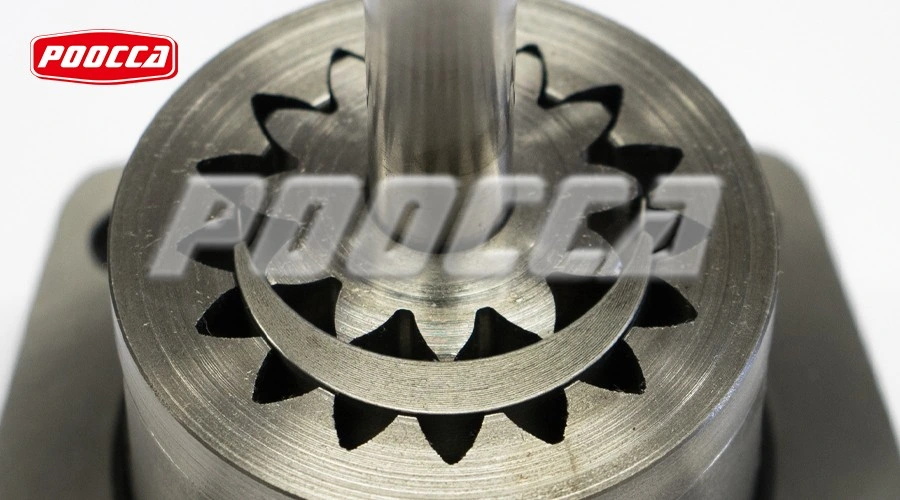
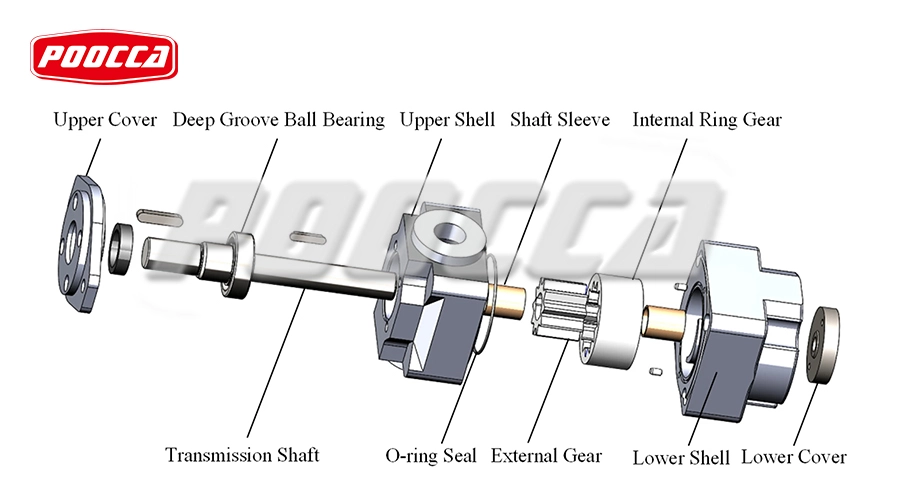
Key Components and Their Functions
The rotor, mounted off-center, drives the idler gear which is positioned within it. The crescent-shaped spacer separates the gears to create suction and discharge chambers, ensuring that fluid moves smoothly through the pump. The casing contains the entire mechanism, providing structural integrity and sealing points.
Materials Used in Construction
The durability and performance of Internal Gear Pumps are significantly influenced by the materials used in their construction. These pumps are generally fabricated from high-strength steel, stainless steel, or cast iron, tailored to meet the specific demands of the application. To boost longevity and operational efficiency, the gears are frequently coated or constructed from materials that resist wear and corrosion, such as bronze or composite substances.
Fluid Flow Path in Internal Gear Pumps
Movement and Distribution of Fluid
Entry and Suction Process
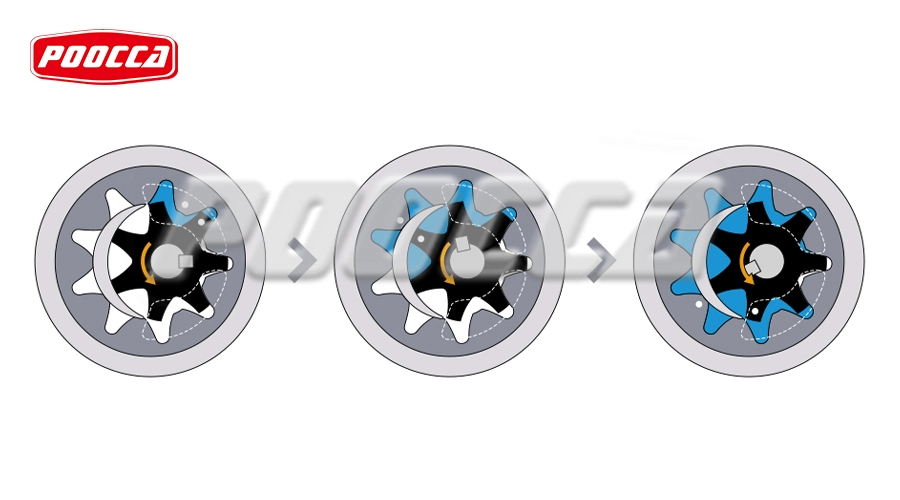
The fluid flow in an Internal Gear Pump begins at the inlet port where the gears create a suction effect. As the rotor turns, it moves away from the idler gear, expanding the cavity and reducing the pressure, thereby drawing fluid into the pump. This initial phase is critical as it ensures an adequate supply of fluid without causing cavitation or undesirable fluid turbulence.
Transition Through the Gears
Once the fluid is drawn into the pump, it gets trapped in the cavities between the gears and the crescent spacer. During the rotation, the fluid is carried around the periphery of the gears without losing volume. This unique gear arrangement allows for a smooth and controlled transition of fluid, minimizing pulsation and ensuring a steady flow rate through the pump’s cycle.
Discharge and Completion Route
As the gears continue to rotate, they eventually reach the discharge side where the cavity between the gears decreases. This compression forces the fluid out of the cavities and into the discharge port. The precision of this discharge process ensures that the fluid flow remains consistent and efficient, contributing to the pump’s overall performance and reliability.
Factors Affecting Fluid Dynamics in Internal Gear Pumps
Viscosity and Temperature Variations
The viscosity and temperature of the fluid being pumped can greatly affect the performance of an Internal Gear Pump. Fluids with higher viscosity need more power to be moved through the pump but take advantage of the pump’s positive displacement properties. Changes in temperature can modify fluid viscosity, requiring adjustments to maintain optimal flow dynamics. It is essential to ensure that the pump material can endure these variations to sustain efficient operation.
Impact of Speed and Pressure Settings
The speed at which the Internal Gear Pump operates, along with the pressure settings, affects the fluid dynamics within the system. Higher speeds can increase the flow rate but may also introduce potential issues like increased wear and reduced efficiency. Conversely, operating at lower speeds can enhance efficiency for high-viscosity fluids but may reduce overall throughput. Proper calibration of speed and pressure settings is essential to strike a balance between performance and longevity.
Exploring Efficiency and Performance Metrics
Understanding Volumetric Efficiency
Volumetric efficiency is a key performance metric for Internal Gear Pumps, reflecting the ratio of the actual volume of fluid delivered to the theoretical volume the pump can handle. High volumetric efficiency indicates minimal internal leakage and superior performance. Factors contributing to high volumetric efficiency include precise gear tolerances, effective sealing, and optimal speed and pressure settings.
Minimizing Leakage and Losses
Minimizing internal leakage and mechanical losses is crucial for the efficient operation of an Internal Gear Pump. This involves ensuring tight clearances within the gear assembly and using high-quality materials and coatings to reduce wear and tear. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the pump’s components can also help in detecting early signs of wear, thereby minimizing potential losses and enhancing the overall efficiency of the pump.
Grasping the intricacies of fluid flow dynamics within an Internal Gear Pump necessitates a deep understanding of its structure, working principles, and the multitude of factors that affect its functionality. Enhancing these components can lead to remarkable efficiency in internal gear pumps, rendering them crucial for a wide array of industrial uses.
Practical Applications and Uses of Internal Gear Pumps
Industrial Applications
The Internal Gear Pump finds extensive use in various industrial applications due to its versatility and efficiency. In the chemical industry, these pumps are essential for handling high-viscosity fluids and hazardous chemicals, ensuring precise and safe fluid transfer. In the paint and coatings sector, the pump’s ability to maintain a smooth and consistent flow is crucial for achieving high-quality finishes. Additionally, in the food and beverage industry, internal gear pumps are used to transport syrups, oils, and other high-viscosity food products without contamination, thanks to their hygienic design and materials.
Automotive Systems
In automotive systems, the Internal Gear Pump is integral for lubrication and hydraulic functions. These pumps are often utilized in automatic transmission systems to ensure smooth gear shifts and consistent operation. They also play a role in lubrication systems, providing a steady supply of oil to critical engine components, reducing wear and enhancing engine longevity. The pump’s efficiency and reliability are vital for maintaining optimal performance in vehicles, contributing to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Agricultural Equipment
Agricultural equipment benefits significantly from the use of Internal Gear Pumps. These pumps are used in hydraulic systems within tractors, harvesters, and other machinery, providing the necessary power for lifting, steering, and other hydraulic functions. The ability to handle a wide range of viscosities and deliver a consistent flow makes them ideal for agricultural applications where fluid properties can vary. This ensures reliable operation and longevity of the equipment, enhancing productivity and reducing maintenance downtime for farmers.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guidance
Regular Maintenance Practices
Inspecting Components
Regular examination of the parts of an Internal Gear Pump is essential for preserving its efficiency and extending its lifespan. Checking the gears, bearings, and seals for indications of wear or harm can avert possible malfunctions. Consistent visual inspections can detect misalignments or unusual wear patterns that may point to deeper problems, facilitating prompt corrective measures.
Lubrication Tips
Proper lubrication is essential for the efficient operation of an Internal Gear Pump. Using the right type of lubricant and adhering to the recommended lubrication intervals can significantly extend the life of the pump. Ensuring that the lubricant is clean and free from contamination is equally important, as impurities can cause excessive wear and reduce the pump’s efficiency. Monitoring lubricant levels and quality should be a routine practice to maintain optimal performance.
Common Issues and Their Solutions
Common issues with Internal Gear Pumps include cavitation, excessive noise, and reduced flow rate. Cavitation can occur when there is insufficient fluid at the inlet, leading to the formation of air bubbles that can cause damage. Ensuring adequate suction pressure and avoiding high-viscosity fluids at low temperatures can mitigate this issue. Excessive noise often indicates wear in gears or bearings, and replacing these components can restore normal operation. A reduced flow rate might be due to internal leakage or worn components, both of which can be addressed through regular maintenance and prompt replacement of faulty parts.
Introducing POOCCA: A Leader in Pump Technology
About POOCCA
Company Background
POOCCA is a renowned company specializing in the design and manufacture of high-quality pumps, including the Internal Gear Pump. With a long-standing history in the pump industry, POOCCA has established itself as a leader through innovation and a commitment to excellence. Our extensive product range and customized solutions cater to various industries, ensuring reliable and efficient fluid handling.
Poocca gear pump manufacturer sells internal gear pumps, Sunny HG gear pumps, Rexroth PGH gear pumps, Eckerle EIPC QT EIPS gear pumps, and more internal gear pumps. We have them for sale. Contact Poocca now to buy.
In addition, external gear pumps are also available for sale, Marzocchi GHP ALP, Shimadzu SGP, Hydromax HGP gear pumps, and gear pumps of various displacement sizes to meet your equipment applications.
Key Strengths and Innovations
POOCCA‘s key strengths lie in our advanced engineering capabilities and rigorous quality control processes. Our pumps are designed to deliver high performance and durability, even in the most demanding applications. Innovations such as anti-wear coatings, precision-manufactured components, and energy-efficient designs set POOCCA apart from competitors. Our focus on sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of our products also aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions in fluid handling.
Conclusion: Essential Takeaways on Fluid Flow Dynamics
Understanding the fluid flow dynamics in an Internal Gear Pump is fundamental for optimizing its performance across various applications. By comprehending the anatomy, operational mechanisms, and factors that influence its functionality, users can ensure efficient and reliable pump operation. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential practices to mitigate common issues and prolong the lifespan of the pump.
The practical applications of Internal Gear Pumps span multiple industries, reflecting their versatility and reliability. Whether in industrial settings, automotive systems, or agricultural equipment, these pumps deliver consistent and efficient fluid handling solutions. Companies like POOCCA continue to lead the way in pump technology, offering innovative and durable products that meet the evolving needs of different sectors.
By integrating best practices in maintenance and leveraging advancements in pump technology, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and ensure the longevity of their equipment. The future of fluid handling looks promising with continued technological advancements and a focus on sustainability, underscoring the critical role of Internal Gear Pumps in modern industry.